Trusts
Terms and Terminologies
a) Author of the trust: he is a person who creates a trust. The property or other assets mentioned in the trust deed belongs to the author of the trust. Author of the trust is also known as Settlor or Grantor.
b) Trustee: he is a person on whom the author of the trust places the responsibility of managing the trust and executing the trust deed.
c) Beneficiary of the trust: it refers to an individual who benefits from the transfer of the property or assets under the trust.
d) The subject matter of the trust is the trust property or trust money
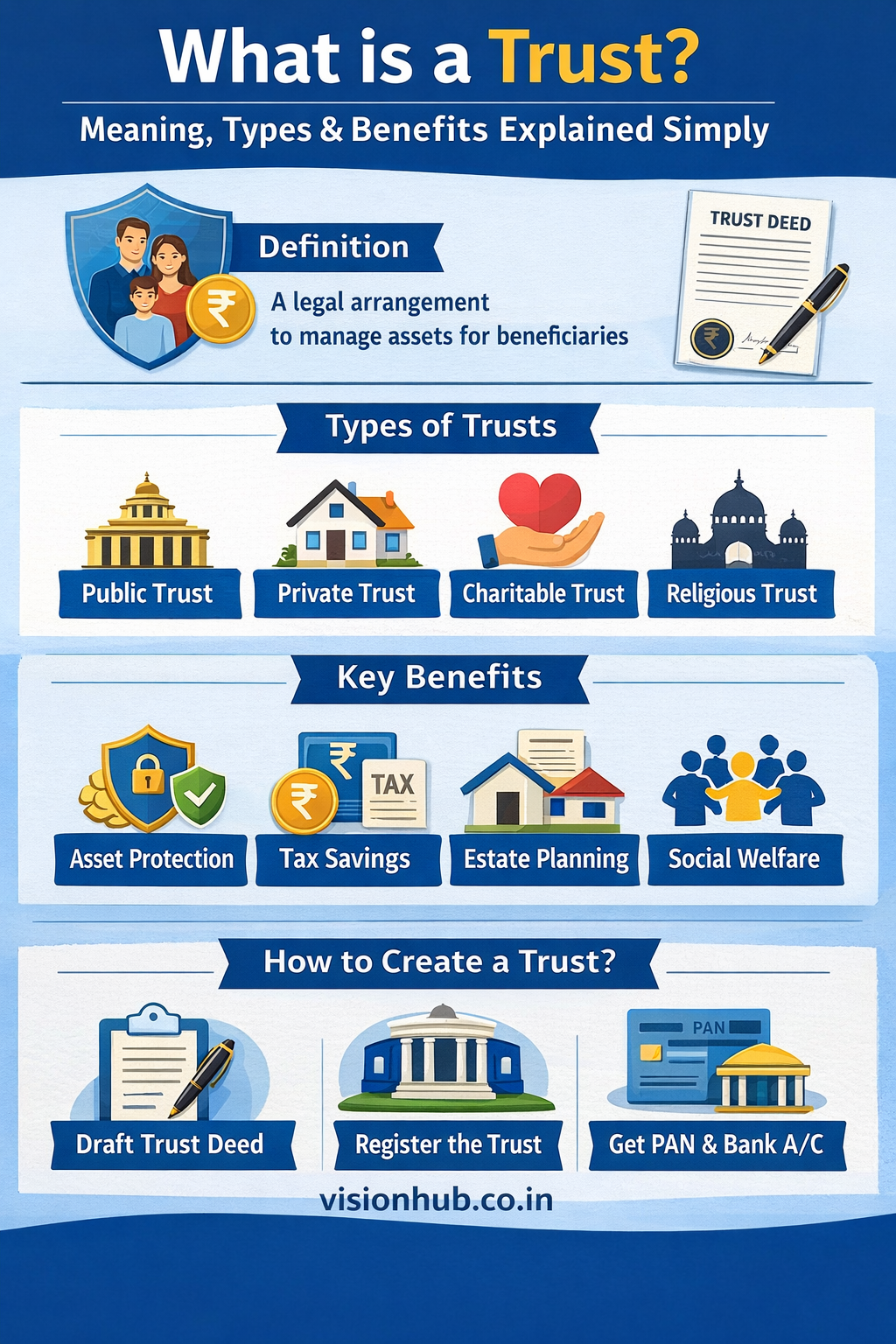
What is a Trust ?
• A trust is simply a legal arrangement / vehicle in which the Settlor transfers ownership of property and other assets to the trust, the named trustee then manages and controls the assets for the benefit of the named beneficiary.
Why a Trust is created ?
a) Private trusts are created to specifically earmark funds intended for minor children, elderly parents, disabled dependents and other beneficiaries.
b) The main advantage of creation of a trust is that the property passes on directly to the beneficiary absolutely hassle free.
c) Another reason for creating trusts can be to deny beneficiaries direct access to funds which they may squander away, while ensuring adequate income flows from it for their maintenance.
d) A trust can be a valuable succession planning tool in many situations, but many do not know exactly how creating a trust may benefit their estate.
For the more affluent, who own businesses governed by families, a trust is a vehicle that provides effective and hassle free wealth management, asset protection and tax efficiency.
Reasons for forming Trusts
• Specific use earmarking
• Assets pass directly to beneficiaries
• Prevents squandering of funds
• Good tool for succession plng
Types of Trusts
a) A trust structure comes with certain inherent advantages. A trust provides the flexibility to be set up in more than one form or in hybrid forms as per the requirement.
b) A trust can be either private or public. A private trust is a trust generally for the convenience and support of individuals of families.
c) Trust can also be structured as revocable or irrevocable.
d) A revocable trust can enable the settlor to exercise control over the property but can be prone to clubbing provisions under the tax laws.
e) An irrevocable trust can provide safeguard against future creditor claims on the assets in case of, bankruptcy, since the settlor ceases to have the title to the trust property, yet at the same time enable indirect control over the property through terms of the trust deed. This is one of the main benefits of a trust structure which allows for preservation of your wealth.
Trust Type as per Structure
Private
Public
Trusts Type as per Assets Accessability
Revocable
Irrevocable
How a trust can be created ?
a) A living trust is a trust that is created while the settlor is still living, and in that case, they may also be the trustee as well as the beneficiary until a triggering event, such as their incapacitation or death, after which named successors take over. This allows a living trust to also act as a mechanism for managing finances in the event you can no longer manage them on your own.
b) A trust can be also formed according to instructions in a will. This is known as a testamentary trust.
c) Assets that can be transferred and owned by a trust include real estate, stocks, bonds, valuable personal property and businesses. A trust, in relation to an immovable property, must be in writing and registered.